3 Min readArticle02 Aug 2021
As OPEC+ Output and Oil Demand Shift, Traders Turn to Micro Futures
At a Glance
One of the beauties of the crude oil market specifically, and commodity markets in general, is that active traders and investors only have one equation to analyze: supply versus demand. It’s a matter of looking at how much product is out there and how much of the supply consumers want right now. That isn’t to say that there are not complex dynamics around each of those two inputs, but it all boils down to simple economics 101. There are no earnings misses, no stock splits, no executive scandals, no rebalancing (as in ETFs)… just supply and demand.
The Pandemic and Driving Season
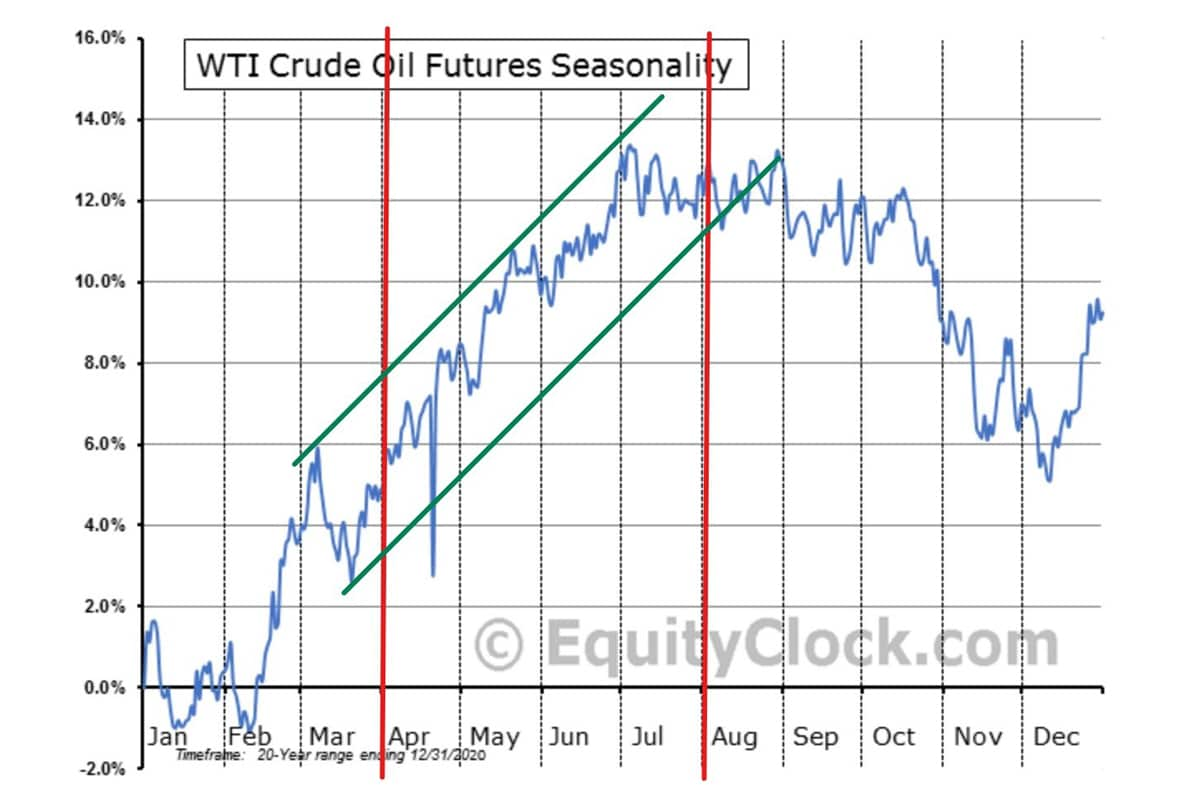
But complex dynamics and forces – whether manmade or otherwise – have the power to alter both supply and demand. Take, for example, the pandemic-induced drop in demand for crude oil, which turned out to be temporary and has almost fully recovered. There are also seasonal demand swings for crude, clearly exemplified by the well-known “summer driving season.” You can see this seasonal price action and the impact of the summer driving season in the chart below.
While the above seasonality chart represents 20 years of price action, it does not reveal a foolproof trading strategy. It is just another piece of the demand equation. For example, the chart above seems to imply that if you buy WTI crude in mid-March and sell in late July, your trade would be profitable. But that is not always the case, as evidenced by a move lower during this period in 2015 and shown in this WTI futures chart.
OPEC and Supply Volatility
There are, of course, other factors that can affect short-term demand, but demand historically has made more gradual shifts. Supply, on the other hand, tends to be the more volatile part of the equation. Recently, the market experienced a bout of supply volatility brought on by uncertainty from OPEC and their allies (now referred to collectively as OPEC+).
In April of 2020, in response to the lockdown-induced decrease in demand, OPEC+ announced the biggest production cut in its history, or almost 10 million fewer barrels per day. (However, they eventually landed on cuts of about 5.8 million barrels per day.) One year later, as economies started to emerge from the pandemic lockdowns, demand and WTI futures prices were both up, prompting OPEC+ to commit to gradually curbing those output cuts. The number of barrels being put back in the market would be decided upon at future meetings, as Saudi Arabia has previously encouraged allied partners to remain cautious on production policy, while warning against complacency as it tries to manage a full price recovery in the oil market.
Agreements on output increases between the members of the cartel were easy to come by until the July 2 meeting concluded with no agreement. It had been widely reported that OPEC+ would be increasing production by 400,000 barrels per day, but the United Arab Emirates wanted more and blocked the agreement. WTI crude jumped 2.4%, with much of the move coming late in the day once the market realized there would be no agreement before the weekend.
The volatility continued over the next seven sessions, with several moves of 1% - 2% or more, keeping many active traders out of the market simply because of the risk of such wide ranges.
Micro Futures Arrive
Then on July 12, CME Group launched Micro WTI Crude Oil futures, which are one-tenth the size of the standard contract. A trader could more finely tune their opinion that a deal between the two OPEC members was inevitable given the demand pressures. The smaller-sized contract allowed easily established short positions with reasonable stops to be placed above the highs of the new range, which was anywhere from $2 to $4 away, depending on where someone placed their short trade entry. That translated into $2,000 to $4,000 risk in the standard contract and $1,000 to $2,000 in the E-Mini Crude Oil futures contract. With the Micro, however, it would only be $200 to $400 of risk.
As many expected, a deal was eventually reached within OPEC that would ramp up production by 400,000 barrels a day each month beginning in August of this year and fully phase out the pandemic-fueled cuts by September 2022. On news of the expanded supply – coupled with new threats to demand from the Delta COVID-19 variant – crude quickly sank 7.28% in just one day. The possibility of that kind of one-day move is exactly what caused many traders to fear looking into a well-researched crude oil trade. The new CME Group Micro WTI Crude Oil futures contract offers a more precise way to participate in these markets.
OpenMarkets is an online magazine and blog focused on global markets and economic trends. It combines feature articles, news briefs and videos with contributions from leaders in business, finance and economics in an interactive forum designed to foster conversation around the issues and ideas shaping our industry.
All examples are hypothetical interpretations of situations and are used for explanation purposes only. The views expressed in OpenMarkets articles reflect solely those of their respective authors and not necessarily those of CME Group or its affiliated institutions. OpenMarkets and the information herein should not be considered investment advice or the results of actual market experience. Neither futures trading nor swaps trading are suitable for all investors, and each involves the risk of loss. Swaps trading should only be undertaken by investors who are Eligible Contract Participants (ECPs) within the meaning of Section 1a(18) of the Commodity Exchange Act. Futures and swaps each are leveraged investments and, because only a percentage of a contract’s value is required to trade, it is possible to lose more than the amount of money deposited for either a futures or swaps position. Therefore, traders should only use funds that they can afford to lose without affecting their lifestyles and only a portion of those funds should be devoted to any one trade because traders cannot expect to profit on every trade. BrokerTec Americas LLC (“BAL”) is a registered broker-dealer with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission, is a member of the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority, Inc. (www.FINRA.org), and is a member of the Securities Investor Protection Corporation (www.SIPC.org). BAL does not provide services to private or retail customers.. In the United Kingdom, BrokerTec Europe Limited is authorised and regulated by the Financial Conduct Authority. CME Amsterdam B.V. is regulated in the Netherlands by the Dutch Authority for the Financial Markets (AFM) (www.AFM.nl). CME Investment Firm B.V. is also incorporated in the Netherlands and regulated by the Dutch Authority for the Financial Markets (AFM), as well as the Central Bank of the Netherlands (DNB).