- 7 Jun 2023
- By CME Group
CME Group provides the F-TIIE futures contract which is an excellent hedge to BONDES that currently represent 22% of the Mexican peso-denominated sovereign debt market. Issued by the Mexican Treasury, BONDES currently represent 22% of the Mexican peso-denominated sovereign debt market with $132 billion USD equivalent outstanding. BONDES are popular and highly liquid floating rate notes with coupons based on Banxico’s F-TIIE rate and can be hedged using CME F-TIIE futures as demonstrated in this paper.
Final coupon calculations are made by assigning overnight F-TIIE rates to each day in the coupon period, including weekends and holidays, and then compounding such rates daily to calculate an annualized rate for the coupon period. The rate is then applied over the four-week or 28-day period to generate a coupon cash flow. Rates assigned to weekends and holidays are based on the prior published daily rate.
This method of coupon calculation is mirrored in the CME F-TIIE contracts, as seen in the whitepaper on settlement calculation. The similarities of both the index and the compounding calculation make CME F-TIIE futures ideal instruments to hedge future BONDES cash flows or to price the value of outstanding bonds.
This paper examines how CME F-TIIE futures can be used to effectively hedge changing overnight F-TIIE rates and to lock in the value of BONDES coupons, as implied by the purchase price.
To determine the correct number of F-TIIE futures contracts required to hedge a BONDES position per month, we need to calculate hedge ratios. To do that, we want to find the equivalent notional value between the BONDES position and the F-TIIE futures position.
Monthly F-TIIE contracts are defined by the value of the IMM index at 20,000 MXN per 1%. This is often expressed in terms of basis points (1/100 of 1%) and is also known as the basis point value or tick value. For F-TIIE contracts, this value is 200 MXN (20,000/100), which can be thought of as the monthly risk per basis point of notional value.

Now let us assume that we have a notional BONDES position worth 1B MXN. The annual risk per bp value is 100K MXN, equivalent to 1/100 of 1% x 1B MXN:

We now have the annual risk per bp for the BONDES position and the monthly risk per bp for the F-TIIE futures. Given that we want to find the monthly hedge ratio, we need to convert the annual figure into a monthly one.
While it may be tempting to simply divide annual risk per bp of the BONDES position – which is 100K MXN – by 12, we can be more precise by using actual number of days in a month to arrive at this figure. The BONDES program uses a 360-day count in its contract, so taking this figure divided by an actual number of days per month gives us our monthly risk per bp of the BONDES position. We will use a month with 31 days as an example.

Our last step is to calculate the hedge ratio between the monthly risk per bp of the BONDES position with that of the futures position.

We can also use these concepts to calculate the notational equivalent of an OTC contract that would change in value by the same amount as the F-TIIE contract (200 MXN per bp per month).

Note that hedge ratios and notional equivalent values will change based on how many days are in the month in question as demonstrated in Exhibit 1 below.
Exhibit 1
MONTH |
DAYS IN MONTH |
Hedge Ratio |
NOTIONAL EQUIVALENT (PER CONTRACT, MILLIONS MXN) |
|---|---|---|---|
January |
31 |
43 |
23.23 |
February |
28 |
39 |
25.71 |
March |
31 |
43 |
23.23 |
April |
30 |
42 |
24.00 |
May |
31 |
43 |
23.23 |
June |
30 |
42 |
24.00 |
July |
31 |
43 |
23.23 |
August |
31 |
43 |
23.23 |
September |
30 |
42 |
24.00 |
October |
31 |
43 |
23.23 |
November |
30 |
42 |
24.00 |
December |
31 |
43 |
23.23 |
Source: CME Group
Using the information in the above table, we can calculate the required number of futures to hedge a position in BONDES and how this affects our trade. Let’s work through an example.
Worked example
Imagine that on May 22, 2023, we own a hypothetical BONDES security maturing on November 30, 2023.
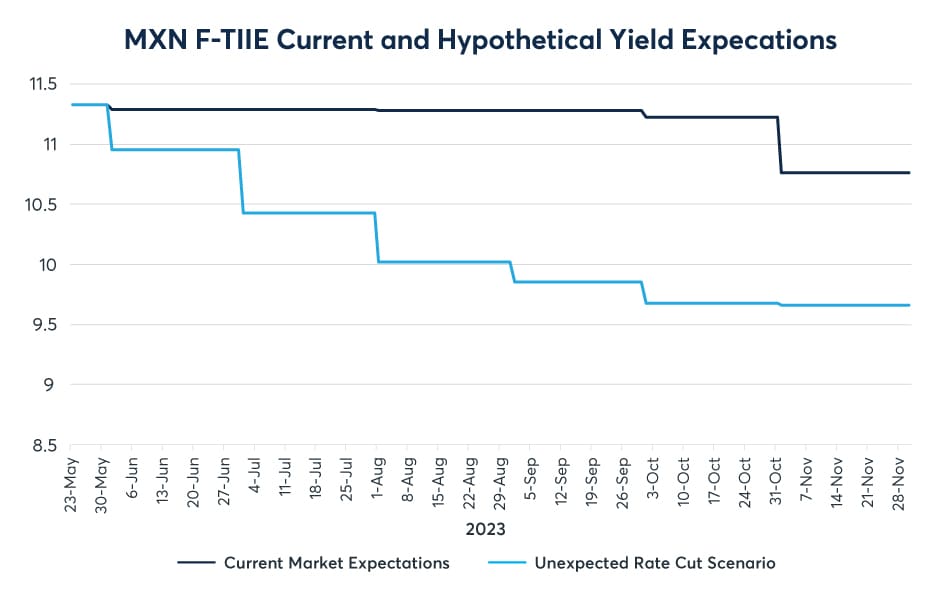
At the time of purchase of the BONDES, the forward interest rate curve is relatively constant around 11.30% with expectations of mild cuts beginning in November as shown by the dark blue line below in exhibit 2.
Exhibit 2
Source: CME Group
If the expectations for interest rates decrease, the value of coupons of our BONDES F position would also fall, if interest rates expectations were to rise then the BONDES F would similarly become more valuable.
The lighter blue line represents a scenario where expectations for interest rates do fall and in fact these new expectations are realised by daily funding rates. In this situation our BONDES F value would be lower than previously. We can hedge this with F-TIIE futures.
As interest rates fall the value of F-TIIE future rises and vice versa. Hence in our scenario we need to buy F-TIIE futures to protect against losses on the BONDES F position in the case where interest rate expectations fall.
The notional of our position in BONDES F is 1bn MXN pesos. In order to hedge we would need to buy futures contracts in each of the next six months until the BONDES maturity date. The number of each contract required can be calculated by taking MXN 1,000 mio and dividing by the notional equivalent for each month per the table in exhibit 1 above. Hence, we get the calculation below:
Exhibit 3
MONTH |
DAYS IN MONTH |
# OF CONTRACTS TO HEDGE 1B MXN BONDES |
FUTURES PRICE AT May 22, 2023 |
|---|---|---|---|
May |
31 |
43 |
88.67 |
June |
30 |
42 |
88.71 |
July |
31 |
43 |
88.71 |
August |
31 |
43 |
88.72 |
September |
30 |
42 |
88.72 |
October |
31 |
43 |
88.78 |
November |
30 |
42 |
89.24 |
Source: CME Group
The expected coupon interest as of May 22, 2023, on the hypothetical MXN 1B notional of BONDES can be seen in the Exhibit 4 table below.
Exhibit 4
Coupon Date |
Days remaining in Coupon |
Coupon implied by daily rates % |
Coupon Interest (MXN Peso) |
|---|---|---|---|
22-May-23 |
|
|
|
15-Jun-23 |
24 |
11.35 |
7,563,947 |
13-Jul-23 |
28 |
11.34 |
8,818,389 |
10-Aug-23 |
28 |
11.33 |
8,815,588 |
7-Sep-23 |
28 |
11.33 |
8,810,546 |
5-Oct-23 |
28 |
11.32 |
8,802,141 |
2-Nov-23 |
28 |
11.23 |
8,737,712 |
30-Nov-23 |
28 |
10.80 |
8,402,745 |
| Total Coupon Interest | 59,951,068 |
||
Source: CME Group
If the revised market expectations are borne out, the coupon interest that would be earned (as depicted by the light blue line in the yield curve chart above) would be lower, as demonstrated in the Exhibit 5 table below.
Exhibit 5
Coupon Date |
Days remaining in Coupon |
Coupon implied by daily rates % |
Coupon Interest (MXN Peso) |
|---|---|---|---|
22-May-23 |
|
|
|
15-Jun-23 |
24 |
11.13 |
7,421,263 |
13-Jul-23 |
28 |
10.75 |
8,362,421 |
10-Aug-23 |
28 |
10.32 |
8,029,254 |
7-Sep-23 |
28 |
10.01 |
7,789,383 |
5-Oct-23 |
28 |
9.86 |
7,665,691 |
2-Nov-23 |
28 |
9.71 |
7,555,163 |
30-Nov-23 |
28 |
9.70 |
7,540,614 |
| Total Coupon Interest | 54,363,788 |
||
Source: CME Group
We see that the total amount of coupon interest earned would be lower by 5,587,280 MXN in the revised market scenario versus the hypothetical starting point.
Had we hedged the change in rates, we would have seen a profit on the F-TIIE futures hedges similar in magnitude to the losses on expected interest.
When market rate expectations were at and around 11.33%, the prices of F-TIIE futures would have been those in the column below labelled “Original Purchase Price.” Similarly, the price of futures implied by the revised market scenario depicted by the light blue line in Exhibit 2 is calculated and displayed in the column labelled “Market Price.”
Note that the quantity of futures that we would have hypothetically purchased is the same as in Exhibit 3 above and is calculated from the notional amount of the BONDES holding. Using the month of June as an example, we can see that this would net MXN 285,600, which is calculated by multiplying the number of contracts by the change in price since purchase by 200 MXN.

The table below shows payouts for each month.
Exhibit 6
Futures as of May 22, 2023 |
# of Contracts |
Original Purchase Price |
Market Price |
Price Change Since Purchase (BPS) |
Payout |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
May |
43 |
88.67 |
88.67 |
0 |
0 |
June |
42 |
88.71 |
89.05 |
34 |
285,600 |
July |
43 |
88.71 |
89.57 |
86 |
739,600 |
Aug |
43 |
88.72 |
89.98 |
126 |
1,083,600 |
Sep |
42 |
88.72 |
90.15 |
143 |
1,201,200 |
Oct |
43 |
88.78 |
90.32 |
154 |
1,324,400 |
Nov |
42 |
89.24 |
90.34 |
110 |
924,000 |
298 |
Total Payout |
5,558,400 |
Readers will note that the futures profits are very close to the loss of interest income on the BONDES F, which was due to the shift in interest rate expectations. Thus, we have executed an effective hedge.
Mexican F-TIIE rate futures at CME Group are an excellent hedge for the interest rate risk variability of BONDES coupons. They allow users to effectively hedge changing overnight F-TIIE rates and to lock in the value of BONDES coupons, as well as potentially speculating on any potential changes in value.
About CME Group
As the world’s leading derivatives marketplace, CME Group is where the world comes to manage risk. Comprised of four exchanges - CME, CBOT, NYMEX and COMEX - we offer the widest range of global benchmark products across all major asset classes, helping businesses everywhere mitigate the myriad of risks they face in today's uncertain global economy.
Follow us for global economic and financial news.